The roundtables aimed to map digital technologies that are enabling circular practices, connecting them across the value chain to foster collaboration among stakeholders and identify challenges and opportunities.
In the first roundtable, the process involved identifying digital technologies that support the circular economy, then mapping these technologies onto the circular value chain to determine their practical applications, and finally sharing specific case studies of how these digital technologies enable the circular economy.
The second roundtable involved, identifying opportunities and challenges to be addressed, along with relevant stakeholders that could collaborate or benefit from these opportunities.
Roundtable 1
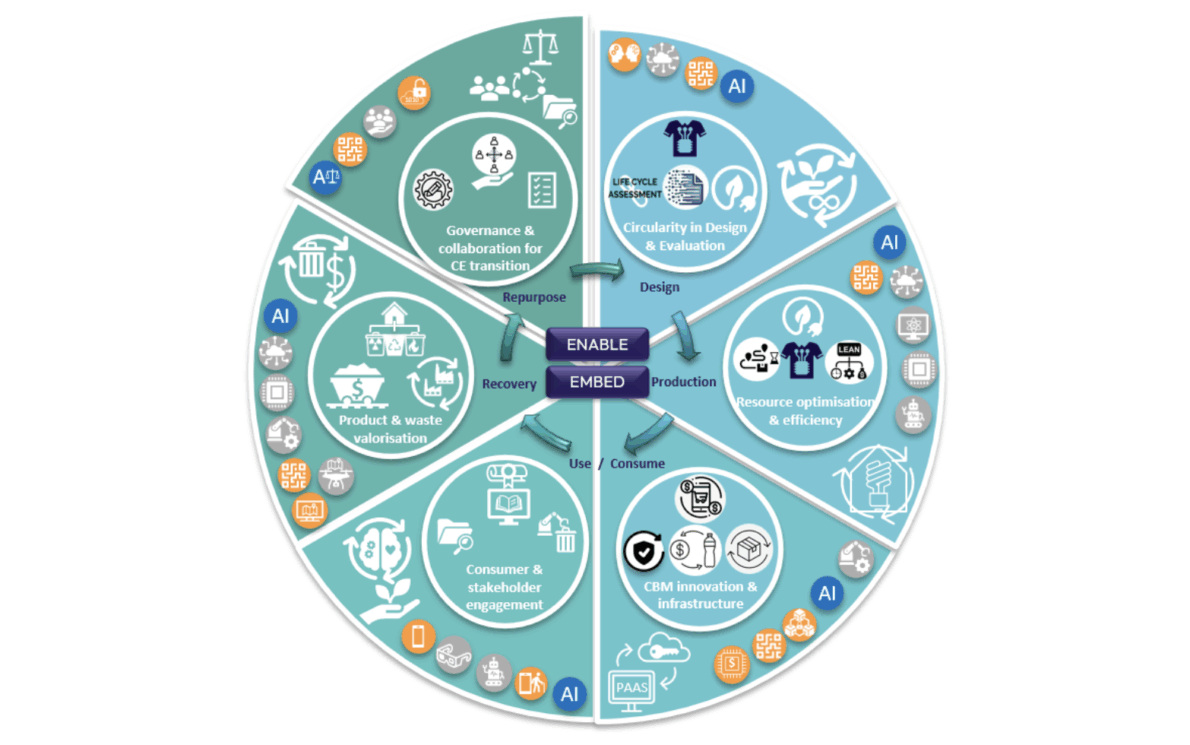
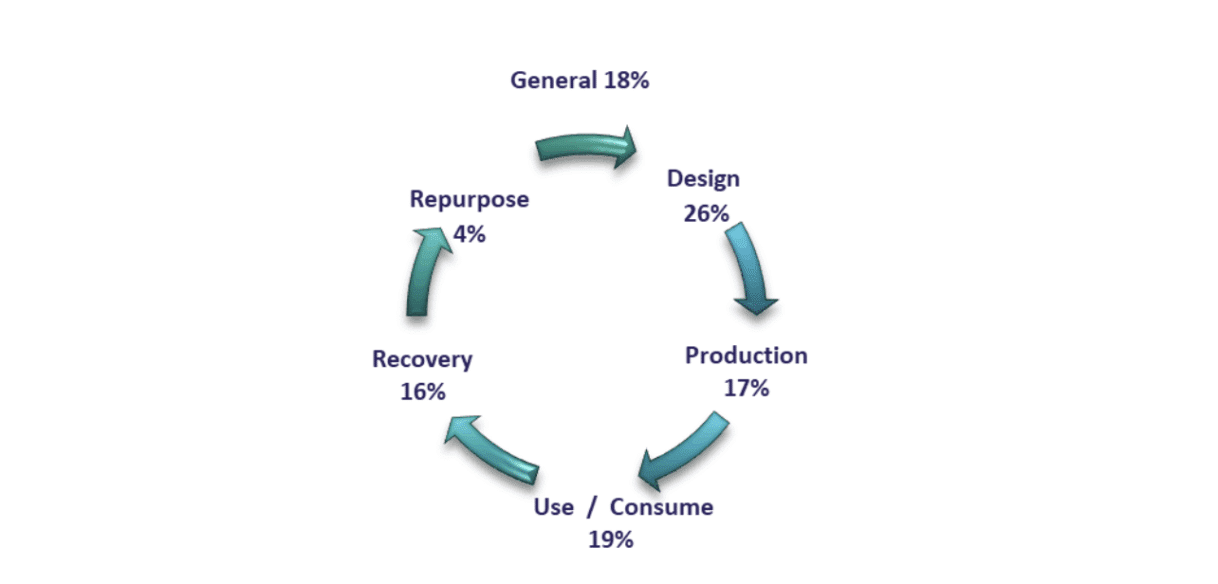
Attendees mapped over 200 resources across the five circular economy value chain phases, including a general phase that encompassed the entire value chain.
The figure below shows attendees focused on the Design, Use/Consume, and Production phases, as well as identifying General resources applicable throughout the value chain. To identify commonalities, these resources were clustered into circular economy strategies enabled by digital technology.
The top circular economy strategies by frequency were:
👫 Consumer engagement (29%) and 🤝 Governance & collaboration for circular economy transition (24%) appear in all phases.
🔄 Product & waste valorisation (19%) mostly appears in the Recovery and Repurpose phase.
💰Circular business model innovation & infrastructure (14%) mostly appears in the Use/Consume phase.
While the Product and waste valorisation opportunities are aligned with the existing academic literature, key practices mentioned leverage digital technologies such as AI, ML, IoT, and digital sensors to identify and repurpose waste, fostering industrial symbiosis and uncovering new resource streams. Consumer engagement, and Governance and collaboration remain as challenge areas recognised by the literature. In terms of Consumer engagement, key opportunities mentioned included raising awareness through social media, immersive technologies (i.e., VR/AR), and storytelling to make circular concepts relatable and actionable. While related to Governance and collaboration, some solutions identified involved establishing systemic design frameworks with ethical standards and supportive legislation for AI-driven decision-making and digital product passports, alongside fostering collaboration across supply chains, academia, and industry clusters to drive innovation, knowledge exchange, and the development of performance-based standards.
Roundtable 2
In the second roundtable, the main challenges mentioned include technical and infrastructural limitations, such as inadequate recycling technologies for diverse materials and the difficulty of redesigning products for disassembly and remanufacturing. Financial barriers are also substantial, with high upfront investment costs for new circular models and a lack of proven profitable business strategies. Furthermore, regulatory and policy frameworks often do not adequately support circular practices, sometimes even incentivizing waste, while consumer behaviour and cultural resistance to reuse and repair models present a major hurdle. Finally, cross-sector collaboration remains a challenge, as the transition requires seamless cooperation across diverse supply chains, industries, and government bodies to establish unified standards, data flow, and shared responsibilities. While the key stakeholders identified were developers, designers, and decision-makers; SMEs, manufacturers, and supply chains; consumers, including the digitally excluded, and society at large; while also mentioning financial institutions.
In both roundtables, digital technologies were seen as enablers, the three digital technology’s themes by highest mentions were:
🔗 Data Sharing and Digital Platforms, including digital twins, blockchain, digital or material product passports, secure, interoperable and traceable data exchange, recommerce platforms, and communication channels. (41%)
🌐 Digital Transformation & Automation, including robotics and automation, internet of things (IoT), advanced computing – quantum and hybrid systems, and data-driven cyber-physical platforms. (37%)
🧠 AI/ML, including agentic AI. (27%)
The three digital technology’s themes appeared in all the circular value chain phases with AI/ML more predominant in Design & Production, while Data Sharing & Digital Platforms appeared less frequently in Recovery and Repurpose, and Digital Transformation & Automation was less prevalent only in Repurpose.
Next steps: developing the Flywheel
All the different circular economy strategies and digital technologies identified can be seen in the first iteration of the DICE Network+ Flywheel, below. We will be developing this visual representation, documenting the specific practices mentioned along with enabling digital technologies in each of the six circular economy strategies in a publication.
Sign up to our newsletter to join us for the upcoming webinar presenting this detail.